Hafnium
Power Additive for Engines and Computer Chips: Hafnium

Hafnium as physical asset
The price development of hafnium, in per cent.
Market Situation
Demand is expected to rise steadily in the coming years due to new, rapidly developing semiconductor technology alone. The significantly growing demand for hafnium for aircraft turbines is also contributing to this development. Following a significant slump due to SARS-CoV-2, aircraft production since the beginning of 2023 has been at roughly the same level as before the pandemic.
Contact Us
Managing Director Matthias Rüth (pictured) and Maximilian Vogler, Manager Private Customers, personally deal with questions and concerns from interested parties.
Phone: +49 (0)69 50 50 250-262
Request Our Digital Info Package
properties of hafnium
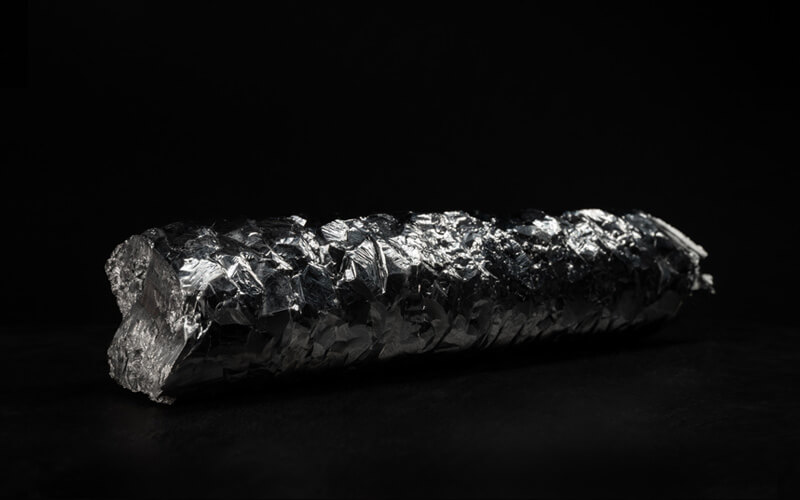

Hafnium is a malleable, silvery metal. Melting and boiling temperatures are very high, and at very low temperatures hafnium is superconducting. Hafnium is a relatively base metal that is very reactive when finely divided and strongly resembles zirconium. When the metal comes into contact with air, a thin oxide layer forms, making it resistant to corrosion.
applications of hafnium
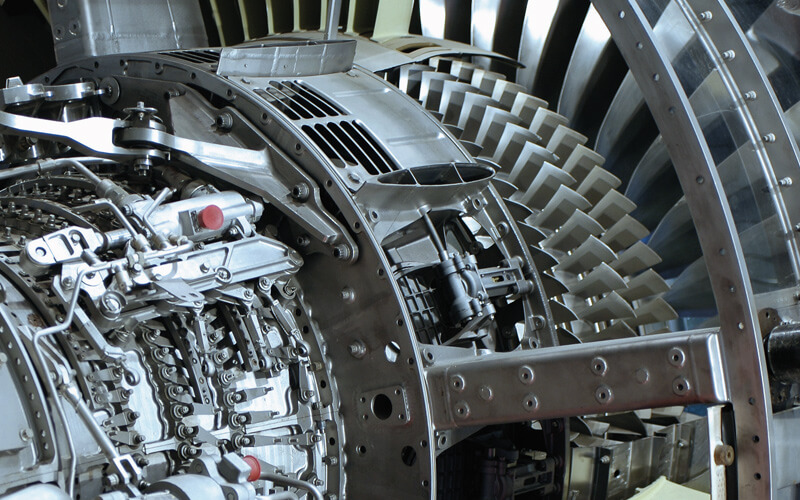
Hafnium is used as a control rod material in nuclear reactors and plays a role in laser technology. Without hafnium, computer chips would be much slower. Fifty percent of total hafnium production alone is used for superalloys in turbines and aircraft technology. For many of these applications, a low zirconium content is important.
There are no independent hafnium deposits, because hafnium always occurs as a companion to zirconium in a proportion of about 1:50. This makes the extraction of hafnium very difficult and extremely costly.